
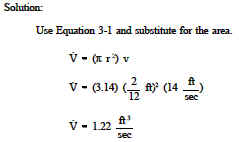
P2 and T2 being the temperature and pressure gas V2 is the volume of the compressed gas P1 and T1 being normal temperatures and pressures v1 is the normal volume (relaxed) Same pressure of 1013 millibars (average atmospheric pressure) for 2 standards:įor calculations of head loss, the size of volumes of gas (compressed or not) moved into the ducts must be given in cubic meters (m3).įor conversions or Nm3 Nm3 m3 / h m3 / h: This is called normal m3.Īttention, there are two standards, and thus potential errors in conversions: Then the temperature and pressure at the time of measurement of the volume, are normalized at called normal conditions. It would be difficult to give a temperature and pressure whenever we speak of a volume of gas.

It becomes very difficult to speak of a quantity of gas volume without giving the pressure and temperature of the gas when the volume was measured. The gas being compressible, it is possible to change a volume of the same amount of gasby compressing or changing its temperature.

The flow of a fluid may be, volume flow or mass flow (that the fluid is incompressible liquid or of constant density, gas) We consider the flow regime is iso-volume or stationary


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
